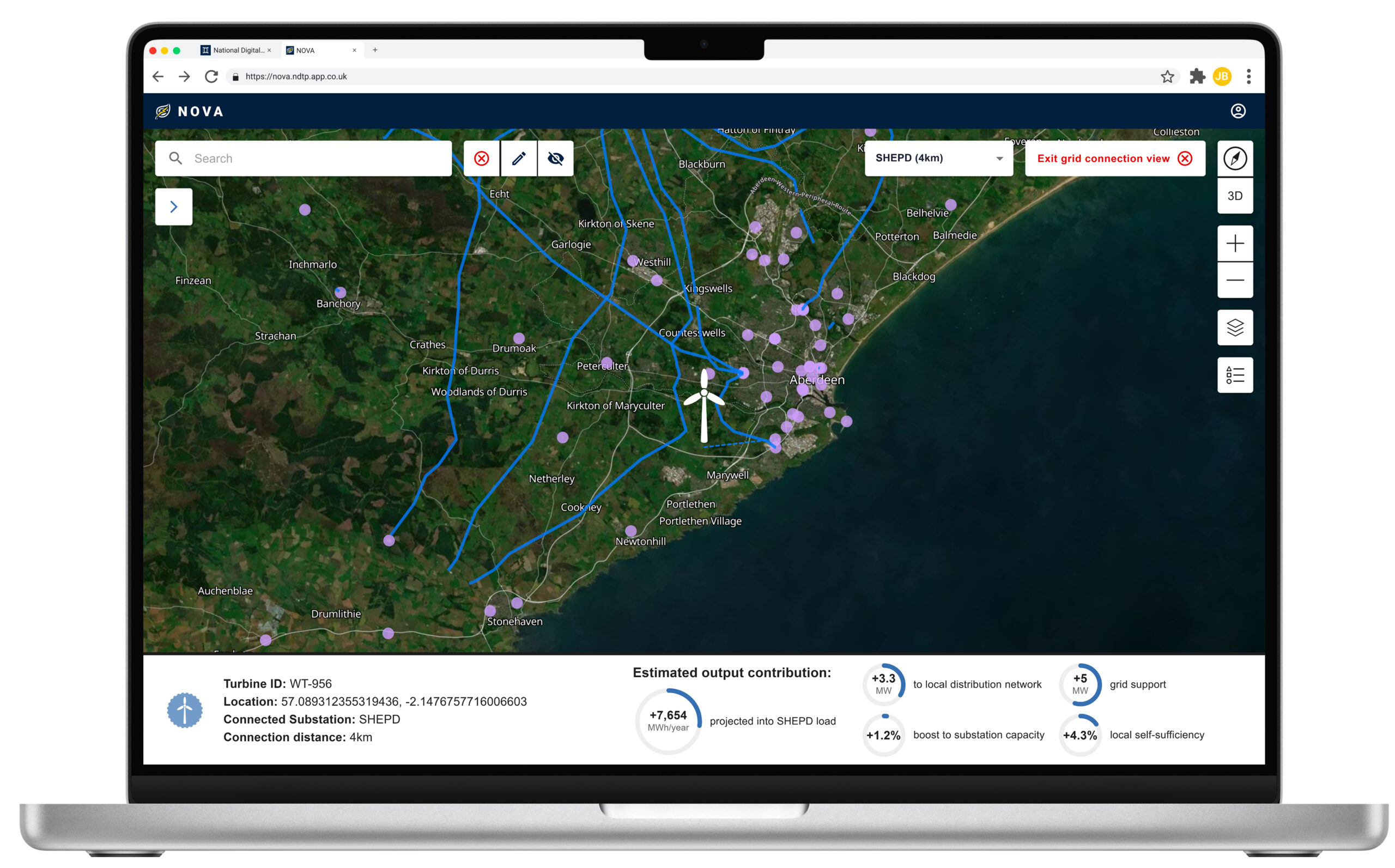
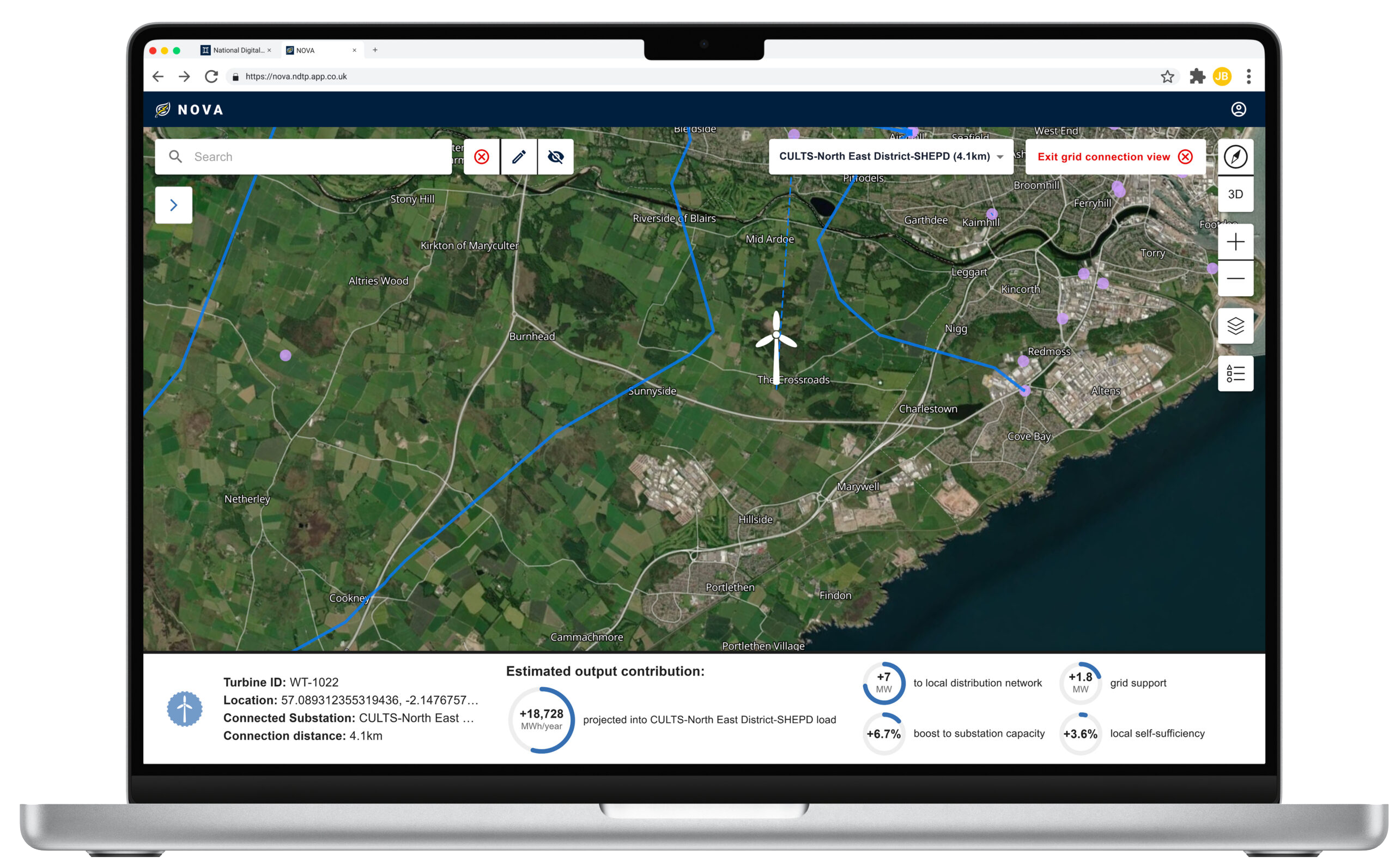
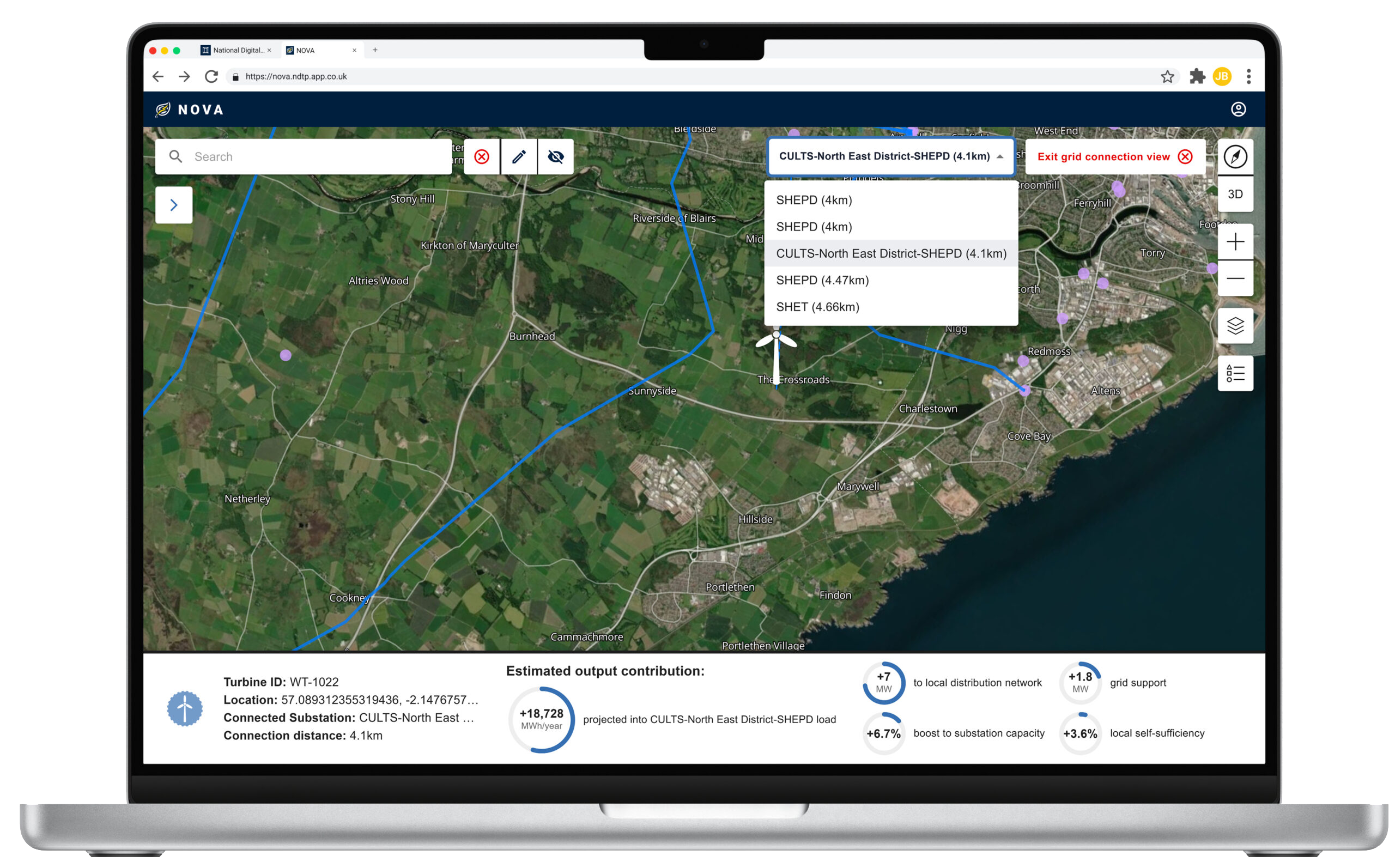
NOVA is an early-stage digital twin demonstrator designed to model and optimise the integration of renewable energy generation and storage on the Isle of Wight. It functions as a digital shadow (see Digital Twin definition for more information), enabling stakeholders to simulate, assess, and refine different energy deployment strategies.

Overview
Current Status
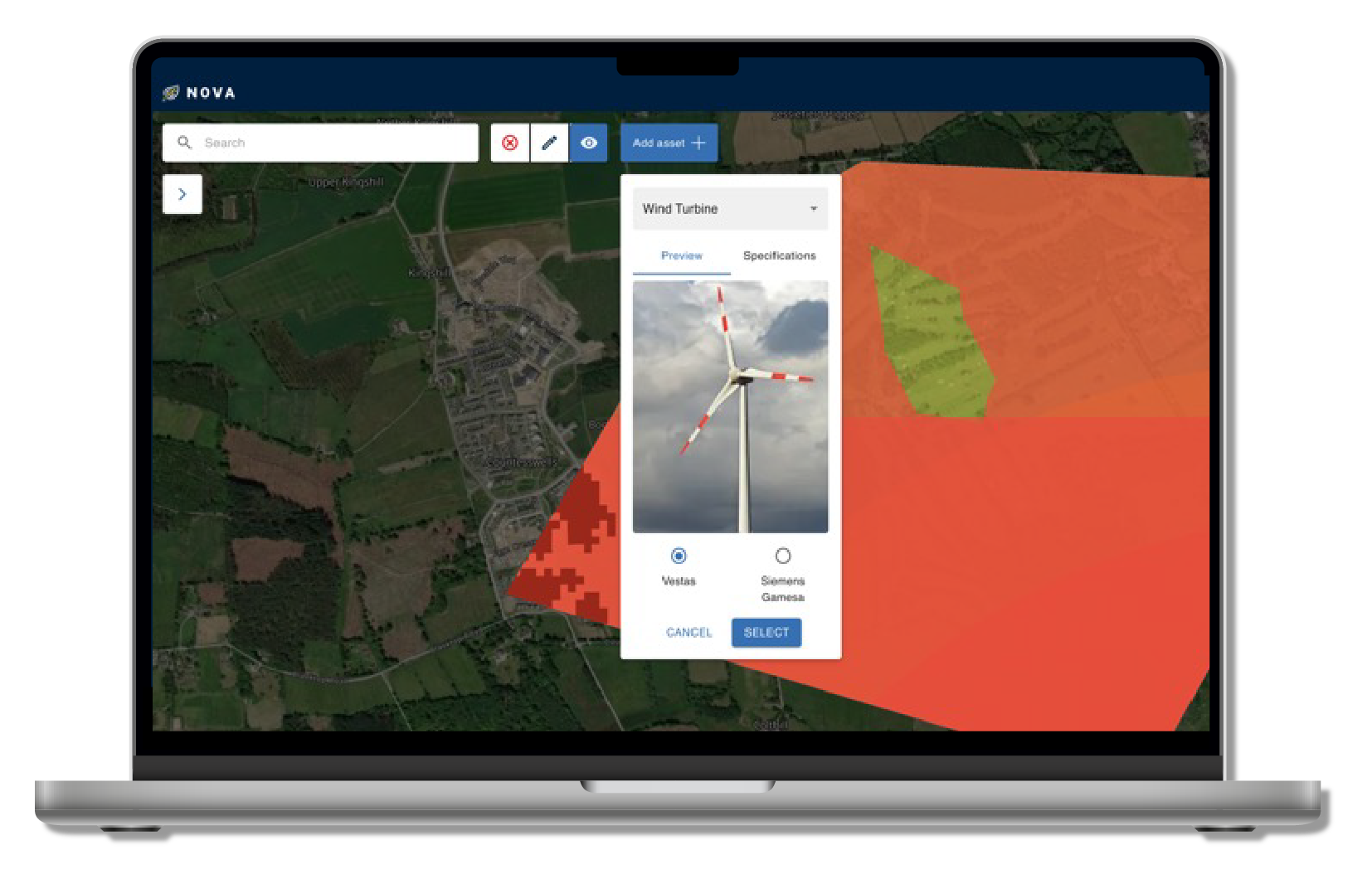
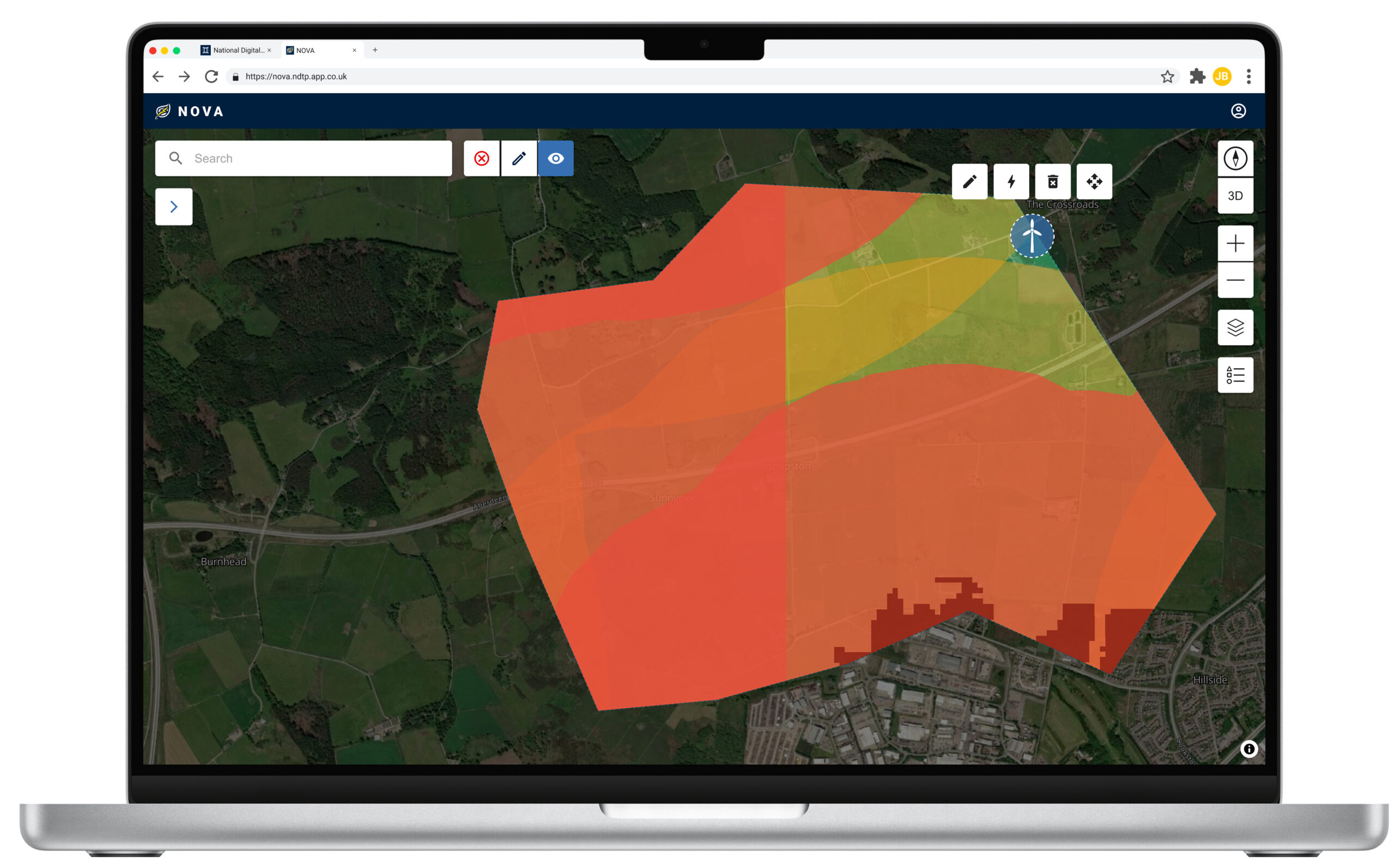
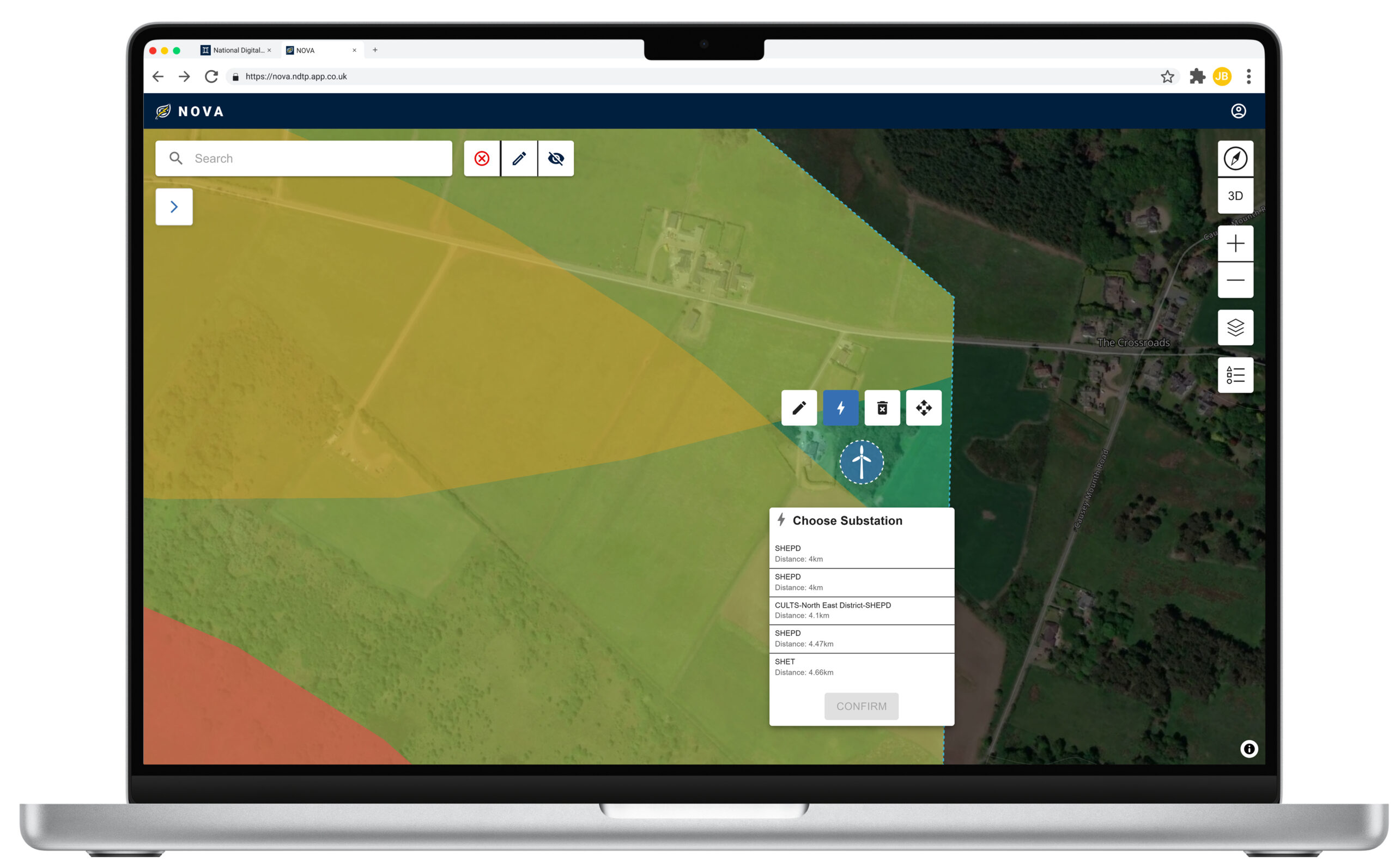
First prototype released for testing – following extensive engagement with energy companies, regulators (e.g. Ofgem), local authorities, and renewable energy developers, the first prototype of NOVA has now been developed and shared with selected test users. This early version focuses on a single asset type (wind) and a small set of data layers, providing a foundation to test the concept and gather feedback. Insights from this phase will help determine the next steps and guide future development towards a nationally scalable solution.
Future Development
The next stage will focus on refining the prototype in response to user feedback, adding further asset types such as solar, tidal, and battery storage, and incorporating more detailed environmental and grid datasets. Future versions will also explore real-time data integration, more advanced grid connectivity modelling, and additional decision-support features.
Note: The NDTP’s collaboration with the National Energy System Operator (NESO), supporting the Virtual Energy System (VES) through collaborative development on the Integration Architecture (IA) is ongoing. For more details on that collaboration, please visit the Collaborations section of our website. While there are overlapping themes in data and scope, NOVA is focused on exploring digital twin applications for renewable energy expansion and grid flexibility at a regional level, with a particular emphasis on the Isle of Wight’s energy transition goals.

What it is
NOVA is an early-stage digital twin demonstrator designed to model and optimise the integration of renewable energy generation and storage on the Isle of Wight. It functions as a digital shadow (see Digital Twin definition for more information), enabling stakeholders to simulate, assess, and refine different energy deployment strategies.
View Explainer Video
Overview
Current Status
First prototype released for testing – following extensive engagement with energy companies, regulators (e.g. Ofgem), local authorities, and renewable energy developers, the first prototype of NOVA has now been developed and shared with selected test users. This early version focuses on a single asset type (wind) and a small set of data layers, providing a foundation to test the concept and gather feedback. Insights from this phase will help determine the next steps and guide future development towards a nationally scalable solution.
Future Development
The next stage will focus on refining the prototype in response to user feedback, adding further asset types such as solar, tidal, and battery storage, and incorporating more detailed environmental and grid datasets. Future versions will also explore real-time data integration, more advanced grid connectivity modelling, and additional decision-support features.
Note: The NDTP’s collaboration with the National Energy System Operator (NESO), supporting the Virtual Energy System (VES) through collaborative development on the Integration Architecture (IA) is ongoing. For more details on that collaboration, please visit the Collaborations section of our website. While there are overlapping themes in data and scope, NOVA is focused on exploring digital twin applications for renewable energy expansion and grid flexibility at a regional level, with a particular emphasis on the Isle of Wight’s energy transition goals.
The problem it addresses
The increasing shift towards decentralised, renewable energy systems presents a significant challenge that demands a nuanced understanding of energy generation, demand, and storage dynamics. As an early-stage digital twin demonstrator, NOVA will address this by modelling renewable energy integration scenarios to assess the feasibility of generating 300MW of new renewable capacity. NOVA aims to explore interactions between diverse generation assets — including wind, solar, and tidal — with battery storage providing flexibility.
The tool will help users understand optimal placement of these solutions within defined geographical areas, accounting for the UK’s ageing grid infrastructure where reinforcements are expensive and time-consuming. This will enable development of sustainable energy portfolios that minimise vulnerability to single-source intermittency while facilitating faster grid connections.
NOVA will provide decision-support tools specifically designed to help planners, regulators, and energy operators optimise investment strategies and infrastructure planning, ultimately facilitating a more sustainable energy transition.
How it contributes to programme vision
NOVA is being designed to support the development of the National Digital Twin Programme’s Integration Architecture (IA) and Information Exchange Standard (IES) by pushing the boundaries of data-integration capabilities. It will contribute by enabling the ingestion of real-time energy data essential for advanced modelling of renewable asset deployment across the UK. The demonstrator may also help extend the IES through the development of domain-specific extensions and by offering opportunities to align the IES ontology with the Common Information Model (CIM).
The demonstrator will require the integration of not only data but models, and will therefore begin to examine the requirements or protocols which need to be introduced to do this successfully.
Who We Are Working With
Lead stakeholders and collaborators
Isle of Wight Council & Local Energy Community Groups
Scottish & Southern Electricity Networks (SSEN)
Renewable energy developers
Regulatory bodies
(Ofgem, DESNZ)
Why We Are Doing This
Testing digital twin capabilities for energy system planning
NOVA is a testbed for digital twin applications in the energy sector, helping to:
- Validate how IA can handle high-volume, real-time energy data ingestion and processing.
- Expand IES to include standardised energy system data models, facilitating cross-sector interoperability.
- Develop new APIs for renewable energy system simulation, integrating data from diverse sources – Energy System.
Supporting the UK’s Net-Zero transition
- Provides strategic insights into renewable energy deployment, guiding local and national grid investment.
- Optimises the use of distributed energy resources, improving grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Enhances energy resilience and flexibility, incorporating battery storage modelling for demand-side management – Energy System.
Key innovations & Next Steps
1. Developing a digital shadow for renewable energy planning
- Integrating geospatial and temporal energy data, enabling scenario modelling for renewables and storage deployment.
- Creating a decision-support tool, helping stakeholders assess the most viable pathways to achieving 300MW of renewable capacity.
2. Refining data-sharing & interoperability
- Enhancing IA’s ability to process large-scale energy datasets.
- Expanding the IES ontology for energy systems, ensuring compatibility with existing national energy datasets.
3. Moving towards experimental prototyping
- Developing an initial interactive prototype, allowing stakeholders to test and refine energy deployment scenarios.
- Engaging with energy regulators and policymakers to align digital twin outputs with future policy needs.
Technical Details
Architecture & Frameworks Used
- Built using NDTP’s Integration Architecture (IA) for scalable, secure, and interoperable data-sharing.
- Designed as a geospatial energy modelling platform, enabling real-time visualisation of renewable energy assets.
Data & interoperability considerations
- Exploring opportunities for enhanced data mapping and ontology alignment by leveraging CIM, a widely used standard in the energy sector, to improve interoperability and consistency across datasets.
- Exploring real-time data integrations, enabling dynamic simulation of energy production and demand scenarios.
Get Involved
As NOVA is still in its early development stage, opportunities to engage are currently focused on shaping requirements and future testing. You can get involved by:
- Providing input on requirements – Organisations with expertise in energy systems, renewables, and grid flexibility can help refine key use cases and data needs.
- Joining the tester community – Once a prototype is developed, early adopters will have the opportunity to trial and validate NOVA’s capabilities in real-world scenarios.
- Sharing knowledge & best practices – Contributions to policy, standards, and interoperability discussions will help ensure that NOVA aligns with existing energy frameworks.
If you’re interested in collaborating, adopting, or contributing, get in touch via ndtp@businessandtrade.co.uk or explore the open-source codebase on GitHub.
Get Involved
As NOVA is still in its early development stage, opportunities to engage are currently focused on shaping requirements and future testing. You can get involved by:
- Providing input on requirements – Organisations with expertise in energy systems, renewables, and grid flexibility can help refine key use cases and data needs.
- Joining the tester community – Once a prototype is developed, early adopters will have the opportunity to trial and validate NOVA’s capabilities in real-world scenarios.
- Sharing knowledge & best practices – Contributions to policy, standards, and interoperability discussions will help ensure that NOVA aligns with existing energy frameworks.
If you’re interested in collaborating, adopting, or contributing, get in touch via ndtp@businessandtrade.co.uk or explore the open-source codebase on GitHub.